What Type Of Muscles Control The Size Of The Bronchioles In Theã¢â‚¬â€¹ Lungs?
Bronchi, Bronchial Tree, & Lungs
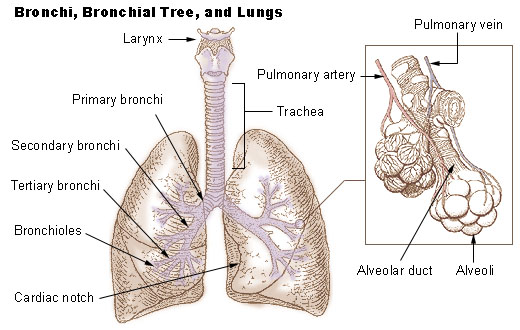
Bronchi and Bronchial Tree
In the mediastinum, at the level of the fifth thoracic vertebra, the trachea divides into the right and left master bronchi. The bronchi branch into smaller and smaller passageways until they terminate in tiny air sacs called alveoli.
The cartilage and mucous membrane of the principal bronchi are similar to that in the trachea. As the branching continues through the bronchial tree, the amount of hyaline cartilage in the walls decreases until it is absent in the smallest bronchioles. Every bit the cartilage decreases, the amount of smooth muscle increases. The mucous membrane as well undergoes a transition from ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium to unproblematic cuboidal epithelium to uncomplicated squamous epithelium.
The alveolar ducts and alveoli consist primarily of unproblematic squamous epithelium, which permits rapid improvidence of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Commutation of gases between the air in the lungs and the blood in the capillaries occurs across the walls of the alveolar ducts and alveoli.
Lungs
The ii lungs, which incorporate all the components of the bronchial tree across the primary bronchi, occupy most of the space in the thoracic cavity. The lungs are soft and spongy because they are mostly air spaces surrounded past the alveolar cells and elastic connective tissue. They are separated from each other past the mediastinum, which contains the heart. The merely point of zipper for each lung is at the hilum, or root, on the medial side. This is where the bronchi, blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves enter the lungs.
The correct lung is shorter, broader, and has a greater book than the left lung. Information technology is divided into iii lobes and each lobe is supplied by one of the secondary bronchi. The left lung is longer and narrower than the right lung. It has an indentation, called the cardiac notch, on its medial surface for the apex of the middle. The left lung has two lobes.
Each lung is enclosed by a double-layered serous membrane, called the pleura. The visceral pleura is firmly attached to the surface of the lung. At the hilum, the visceral pleura is continuous with the parietal pleura that lines the wall of the thorax. The small space between the visceral and parietal pleurae is the pleural cavity. It contains a sparse film of serous fluid that is produced past the pleura. The fluid acts as a lubricant to reduce friction as the two layers slide against each other, and it helps to hold the two layers together as the lungs inflate and deflate.
What Type Of Muscles Control The Size Of The Bronchioles In Theã¢â‚¬â€¹ Lungs?,
Source: https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/respiratory/passages/bronchi.html
Posted by: courtexcirs.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Type Of Muscles Control The Size Of The Bronchioles In Theã¢â‚¬â€¹ Lungs?"
Post a Comment